A simple project that uses Edit Distance Algorithm to identify duplication or redundancy and a way to solve it.
Introduction
Data redundancy occurs when the repeated data is in the dataset, resulting in data inconsistency when the same data appears in multiple tables in different formats. This could be due to things like data entry errors or system error or data collection methods. Data redundancy expands the size and complexity of a database, making it more difficult to manage. Data analysts are unable to extract precise information because of redundant data, which also has an impact on conclusion withdrawal and decision making. In order to reduce the complexity of the dataset, the duplicity and the replication of the data needs to be figured out.
The data redundancy detection system will expose the replication of the data using the technique of string-matching algorithm. This will select the key characteristics from the given dataset and detect the repeating data. Data Redundancy Detection System will be able to take in a large amount of data, scan it using the Duplicate Count Strategy- Multi Record Increase Approach method, and return duplicate data.
Why Data Redundancy Detection System?
The government is the largest producer of data, and the official source of data for development planning, decision-making and accountability. The data produced through official surveys ranges in quality. The frequency of official survey implementation largely depends on the availability of donor funding and so survey data can quickly become out of date. There is some duplication between surveys and the administrative data collected by the ministries, and numerous inconsistencies in the data. Due to the above scenarios occurring in the dataset which may result in storage problems, problem in data analysis and decision making. So, the repeated data must be identified.
With the aim to visualize and extract the duplicity of the data from the dataset, we came up with data redundancy detection system. It will be an automated system to detect the replicated data from the input database and filter the dataset. We present a system that detects redundancy that can be used to clean the data in an automated manner while also visualizing data redundancy. This system can be an approach to optimize the data improving the efficiency, receiving the precise information and suitable decision making via the data analysis which can be obtained by sorting out the redundancy of the data.
This system is designed to use homogeneous source of dataset to find the duplication of data. The algorithm can be classified by the two stages. In the first stage, field matching of each record is performed by using Edit Distance Algorithm. In this system we will only use character-based similarity measurement technique for field matching as in our system, the dataset’s row is converted into string and then is compared for duplicity detection.
In second stage, we use Duplicate Count Strategy (DCS). DCS is variation of Sorted Neighborhood Method (SNM). If a duplicate is found on the sorted dataset, it can also detect the other possible duplicates by comparing the record of that duplicate. After evaluating about the data duplication problem in large data and its impact. We expect our system to extract the redundant data entries from the dataset using the DCSAlgorithm with Edit Distance Algorithm.
Working Mechanism
First, the news dataset was gathered from anonymous source. Then the data was cleaned and preprocessed using string matching technique. Then we have calculated a similarity metric by taking the reference of edit distance algorithm that is commonly used to find similar field items and used the Duplicate Count (DCS) Algorithm for detecting exact duplicate records over provided dataset.
Modules
Edit distance module
An edit distance module is a component of a data redundancy detection system that calculates the number of operations required to transform one string into another string. In the context of data redundancy detection, the module is used to calculate the similarity between two sets of data. This module is used to apply edit distance to find the distance between the data.
def edit_distance(s1, s2):
m = len(s1)
n = len(s2)
# initialize the matrix
d = [[0] * (n + 1) for i in range(m + 1)]
# fill the first row and first column
for i in range(1, m + 1):
d[i][0] = i
for j in range(1, n + 1):
d[0][j] = j
# fill the rest of the matrix
for j in range(1, n + 1):
for i in range(1, m + 1):
if s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]:
d[i][j] = d[i - 1][j - 1]
else:
d[i][j] = min(d[i - 1][j], d[i][j - 1], d[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1
# return the final value in the matrix
return d[m][n]
Finding duplicate module
This module detects duplicates; we identify matching fields and compare data in the dataset.
def count_duplicates(records):
count_dict = {}
for row in records:
record = tuple(row[1:]) # discard column 1
if record in count_dict:
count_dict[record] ['count']+= 1
count_dict[record]['ids'].append(row[0]) # add ID to list of IDs
else:
count_dict[record] = {'count': 1, 'ids': [row[0]]}
duplicates = []
total=0
for record, count_dict in count_dict.items():
if count_dict['count'] > 1:
duplicates.append(f"IDs: {', '.join(str(id) for id in count_dict['ids'])},{record}: duplicate count: {count_dict['count']} ")
total=total+count_dict['count']
lbl_total=Label(window, text="Number of Duplicates")
lbl_total.pack()
lbl_total_count=Label(window,text=total)
lbl_total_count.pack()
return duplicates
Upload file module
This module uses tkinter’s filedialog to ask the user to select a CSV file. Then it reads the selected file using pandas and performs some data cleaning and processing and computes the edit distance between pairs of strings in the data and identifies pairs that have a distance below a certain threshold. It then displays the results in a GUI using tkinter’s Text and Label widgets, including the number of data points, the number of comparisons made, and the list of duplicate data points.
def upload_file():
file=filedialog.askopenfilename(title="Select file" , filetypes=[("All files", '*.*'),("CSV files", '.csv')])
if(file):
lbl_my_file=Label(window, text="File read!", font=("arial", 12, "bold") )
lbl_my_file.pack()
comparison=0
threshold=5
chunk_size=50
canvas = None
probable=[]
probable_dup=[]
matching_ids=[]
df = pd.read_csv(file, infer_datetime_format=True, encoding='ISO-8859-1')
file_name.set(file)
df["name"] = df["name"].str.replace(" ", "")
std = df[['id', 'name', 'age', 'age_unit', 'province_id', 'district_id', 'municipality_id',
'tole', 'ward', 'caste', 'sex']].values
df['std_att'] = df.apply(lambda row: str(row['name']) + str(row['age']) + str(row['age_unit'])
+ str(row['province_id']) + str(row['district_id']) + str(row['municipality_id'])
+ str(row['tole']) + str(row['ward']) + str(row['caste']) + str(row['sex']), axis=1)
std_att = df['name'].astype(str) + df['age'].astype(str) + df['age_unit'].astype(str)
print("............Dataset..........")
for index, row in df.iterrows():
a=f"ID: {row['id']}, std_att: {row['std_att']}"
print(a)
mylist = Text(window)
mylist.pack(side=LEFT, fill=BOTH, expand=True)
# create a scrollbar and associate it with the listbox
sb = Scrollbar(window)
sb.pack(side=RIGHT, fill=Y)
mylist.config(yscrollcommand=sb.set)
sb.config(command=mylist.yview)
mylist1 = Text(window)
mylist1.pack(side=LEFT, fill=BOTH, expand=True)
# create a scrollbar and associate it with the listbox
sb = Scrollbar(window)
sb.pack(side=RIGHT, fill=Y)
mylist1.config(yscrollcommand=sb.set)
sb.config(command=mylist1.yview)
unique_ids = [] # list to store unique IDs
unique_std_att = [] # list to store corresponding unique std_att values
print("...........Edit Distance without sorting: ...........")
for i in range(0, len(df), chunk_size):
chunk = df.iloc[i:i+chunk_size]
std_chunk=std_att.iloc[i:i+chunk_size]
# print(type(chunk)) # add this line to check the data type
m = len(chunk)
for j in range(m):
for k in range(j + 1, m):
id_j = str(chunk.iloc[j]['id'])
id_k = str(chunk.iloc[k]['id'])
dist = edit_distance(std_chunk.iloc[j], std_chunk.iloc[k])
comparison += 1 # m * (m - 1) / 2
if dist == 2 or dist ==1 :
edit = (dist, f"Edit distance between ({id_j}){chunk.iloc[j]['std_att']} and ({id_k}){chunk.iloc[k]['std_att']} : {dist}")
probable_dup.append(edit)
if dist <= threshold:
pair = (dist, f"Edit distance between ({id_j}){chunk.iloc[j]['std_att']} and ({id_k}){chunk.iloc[k]['std_att']} : {dist}")
probable.append(pair)
if id_j not in unique_ids:
unique_ids.append(id_j)
unique_std_att.append((chunk.iloc[j]['id'], chunk.iloc[j]['std_att']))
if id_k not in unique_ids:
unique_ids.append(id_k)
unique_std_att.append((chunk.iloc[k]['id'], chunk.iloc[k]['std_att']))
print("...........Edit Distance in Sorted order.............")
probable = sorted(probable, key=lambda x: x[0]) # sort by distance
for pair in probable:
print(pair[1])
probable_dup = sorted(probable_dup, key=lambda x: x[0]) # sort by distance
mylist1.insert(END,f"Probable Dupliates:\n")
for edit in probable_dup:
mylist1.insert(END,f"{edit[1]}\n")
print("..........Dataset within the edit distance with unique id.............")
print(unique_std_att)
print("Length of unique attribute(edit distance): ", len(unique_std_att))
# print("duplicates: ")
duplicates = count_duplicates(unique_std_att)
mylist.insert(END,f"Exact Dupliates:\n")
for i in range(len(duplicates)):
mylist.insert(END,f"{i+1}: {duplicates[i]}\n" )
lbl_data=Label(window, text="Number of data in dataset:")
lbl_data.pack()
lbl_data_count=Label(window,text=len(std_att))
lbl_data_count.pack()
lbl_comparison=Label(window, text="Comparison")
lbl_comparison.pack()
lbl=Label(window,text=comparison)
lbl.pack()
# create scrollbar
sb = Scrollbar(window)
sb.pack(side=BOTTOM, fill=BOTH)
window.update_idletasks()
canvas.config(scrollregion=canvas.bbox("all"))
Output
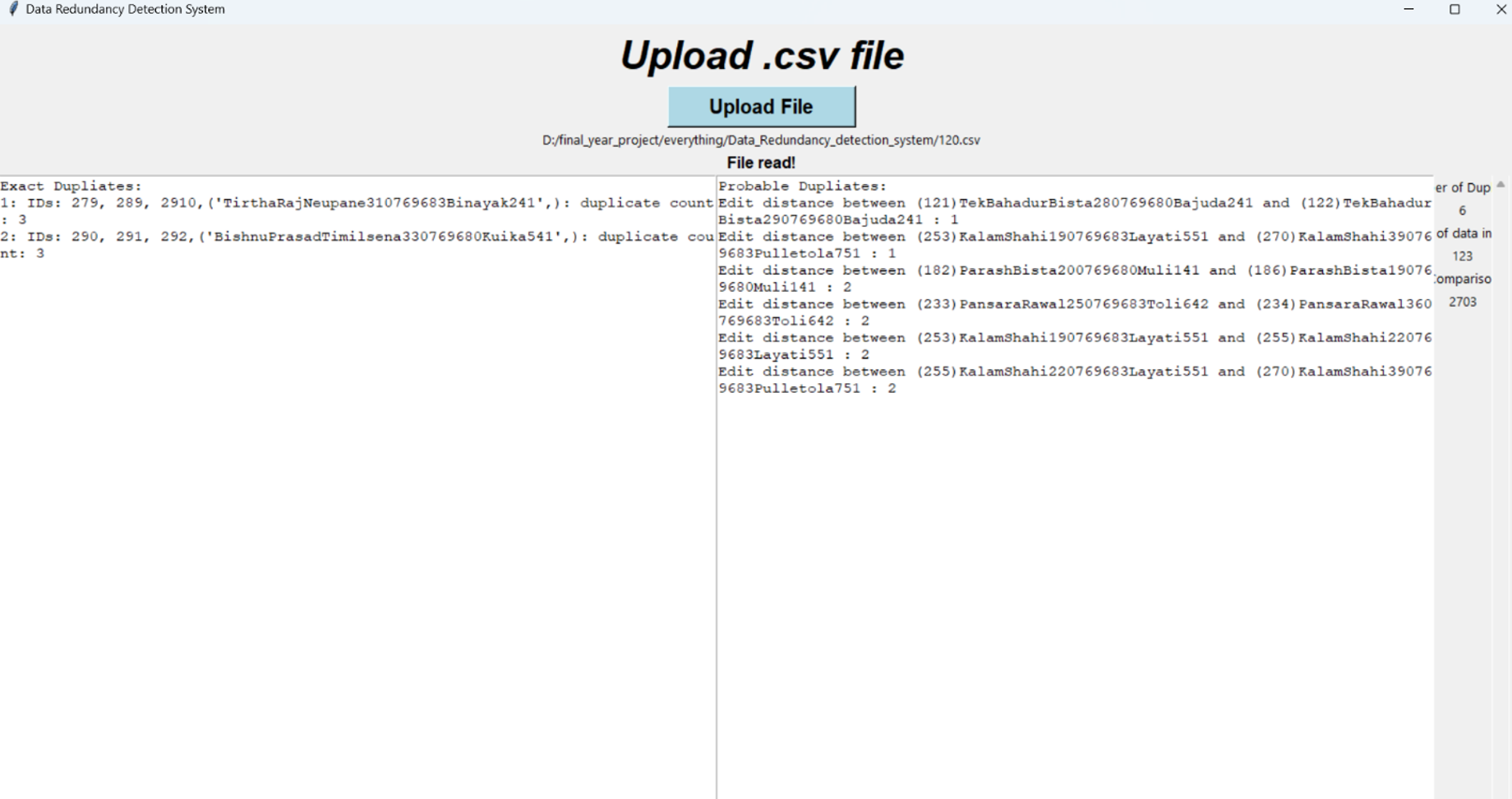
Conclusion
In conclusion, Data Redundancy Detection System will be able to detect the redundant data and the number of the redundant data. Furthermore, the dataset is loaded and preprocessed in chunk for faster processing. Edit Distance algorithm is used for Field Matching. On the basis of the distance between the standard attribute, the data is sorted and similar records are abstracted. Finally, the similar dataset undergoes the duplicate finding strategy i.e., DCS Algorithm and the exact duplicated data and most probable duplicate data will be the resultant. Overall, the project will find the duplicity of the data which can help to minimize the storage issue, accuracy rate of data and give better precision and conclusion of the data.


Leave a comment